First aid refers to medical attention that is usually administered immediately after the injury occurs and at the location where it occurred. It often consists of a one-time, short-term treatment and requires little technology or training to administer, but one must be aware of it. How often have you seen people crowding around a Road Traffic Accident victim, taking photographs, making reels but not helping the victim? Do they even know that a little timely help from them can save the precious life which otherwise is doomed to extinguish?
Thankfully most accidents occur in the home, including cuts, suffocation, bruises, and concussions. It is crucial to know what to do when these things happen, as you never know how long of a time you can allow yourself to wait for the ambulance to arrive. Actions taken immediately after an accident have many a time saved lives or at least decreased the damage of the injury. The things you do right after the accident are extremely important. And so, keep these sets of advice close by, and share it with your loved ones:
Burns
First-degree burns can cause redness of
the skin. 2nd-degree burns may cause blisters, and 3rd-degree burns may
cause blackened skin and damaged deep tissues.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: When it is a 1st or
2nd-degree burn, put it under flowing cool water or put wet towels on the area.
Common house-hold treatments to reduce
pain:
· Pour water on burn. Copious amount, more so if it is a chemical burn, in order to dilute the acid or alkali. However, on the face, protect the eues before irrigating a chemical burn area. The chemical should not reach the eye.
· A soaked tea bag will bring about immediate relief, owing to the healing qualities of Tannins, which are known to shrink tissues. Soak a bag of tea in cold water, and then put on the skin. These are also a great solution for sunburns.
· Uncooked potato: Take off the peel of an uncooked potato, cut it into slices and put on the burned area, so the liquid coming out of the potato will calm down the burn.
What NOT to do: Don't put ice on big
burns. Ice may damage the skin or make the injury worse. You cannot use
antibiotics or butter or toothpaste either.
When to seek medical aid: As soon
as possible, particularly if these are
3rd-degree burns or electrical or chemical burns.
Open Wounds
Open wounds in the skin need to be
quickly treated to prevent infection.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: Place a strip of gauze on
the wound and apply direct pressure to stop the bleeding. If these are minor
cuts and scrapes, wash with water and soap and smear a thin layer of antiseptic
or antibiotic cream, and cover with a band-aid or bandage. If you feel it is a
minor cut and does not warrant medical attention then get a tetanus toxoid
shot.
What NOT to do: Do not wash nor put a
regular cream on a large, deep or very bloody injury. Instead, go seek medic
aid.
When to seek medical aid: If the
wound is deep and becomes infected, accompanied by heat, redness, swelling or
red stripes around, or if it has a foreign object in it (such as a nail) - go
seek medical aid immediately.
A fracture
The fracture on any bone is a serious
injury and requires urgent medical attention. Whether sustained at home or at
roadside you need to go or be taken to a hospital. If the skin over the fracture is intact the
problem is less complicated than if the fracture is accompanied with an
overlying wound.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: Fractures in the limbs
should be splinted immediately so that the underlying muscles, tendons, nerves
and vessels are destroyed no further by the broken bone ends. Fractures of large
bones like in the thigh can be associated with a lot of blood loss around the
fracture even when the patient is not seen actively bleeding outside. A bleeding limb wound requires a tourniquet
to be tied above the site of bleeding and the time of tying the tourniquet should
be noted.
What NOT to do: Don't waste time. Rush to
a hospital. .
When to seek medical aid: Immediately.
Only fractures of small bones of the hand and facial fractures give us
time but weight bearing bones and large bones need urgent attention.
A blow to the head
The skull provides our brain with very
good protection, and so only rarely does it get hurt, but if it is a strong
blow, the neck, back, and soft tissues can get seriously damaged.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: If the person is
unconscious, call an ambulance. If the area looks like it is bleeding, treat it
like a cut but make sure to follow up with a doctor who will check for internal
injuries. You can put a bag of ice on the area to decrease the swelling.
What NOT to do: Don't leave the injured
person alone, especially when they are asleep. Wake them every 3-4 hours and
ask simple questions (‘what time is it?' 'What day/date?' 'What is your name?')
to make sure there is no brain injury or concussion.
When to seek medical aid: If the
person harmed is convulsing, feeling dizzy or nauseous, vomits or displays
obvious changes to behavior or has severe headache.
Suffocation
Suffocation is a rare occurrence and
when it happens it can be deadly. When a person is chocking they cannot cough
strongly enough to breath or talk, and his face will begin to get blue or red.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: Remove the
obstruction if possible. Ensure an open airway to allow the air to reach
the lungs. Place the individual on his back. Support the nape of the neck on
your palm and press the head backwards. Then press the angle of the jaw forward
from behind. This will extend the head on the neck and lift the tongue clear
off the airway. If the airway is opened by this method the individual gasps and
starts to breathe. Give three to four inflations of the lungs to facilitate
breathing by mouth-to-mouth method. If the heart is beating, carotid pulse can
be felt at the base of the neck. (Pulse at wrist may not be felt). Continue to
ventilate the lungs until breathing becomes normal. In order to prevent
damage to the brain and other vital organs (which will occur due to the lack of
oxygen) apply artificial respiration to ensure prompt ventilation of the lungs,
and if necessary, do external cardiac compression. Continue creating an
"artificial respiration" until natural breathing is resumed. It may
be necessary to continue for a while afterwards unless a doctor advises to
stop.
What NOT to do: Do not drink water if
there is a strong cough.
When to see Medical Aid: As soon
as possible.
Poisoning
Possible risks at home include cleaning
materials, Carbon dioxide, and pesticides. Even stings can be poisonous for
some people.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: If a person is unconscious
or is having trouble breathing, you must take them immediately to seek medical
aid. Be prepared to give out the next details quickly: What is the substance
involved, how much was taken, when, what is the weight and age of the person?
What NOT to do: Don't wait for the
symptoms to start to call for help. Don't try to vomit and don't drink
anything, unless a medical professional has told you so.
When to see Medical Aid: As soon
as possible.
An object enters the eye
Anything that enters the eye, whether it
is a grain of sand or a chemical mixture, can cause pain and may harm the
cornea.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: Try to blink the foreign
object away. If it doesn't come out, wash the eye by holding the lid open under
a faucet.
What NOT to do: Do NOT rub your eyes. Even a small amount of dirt may scratch your cornea and
cause infection and irreparable damage. Never try to dislodge a large object
yourselves or an object buried deep in the eye. Leave that for professionals.
When to seek medical aid: If a
chemical material like bleach enters, or it is a large object or one that is
lodged deep in the eye - go to the emergency room immediately. If it is a small
object but it causes swelling or disrupts your vision - call a doctor.
Nose Bleeds
Nose bleeds occur when the gentle blood
vessels inside the nose break. This could happen easily due to weather
conditions, a strong blow or a chronic leaky nose. It can also follow head
injury.
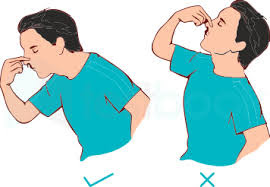
What to IMMEDIATELY do: Sit on a chair and lean
your body forward. Pinch your nose closed right below its bridge, where the
bone meets cartilage. Maintain the pressure for 5-15 minutes. You can also use
an ice pack to keep pressure. If you have a digital blood pressure
instrument then document the blood
pressure and if it is high then take a dose of your prescribed blood pressure
medicine..
What NOT to do: Do not tilt your head
back, as you may swallow the blood, or it may trickle into your windpipe and lungs.
When to seek medical aid: Contact
a doctor if you aren't able to stop the bleeding after 20 minutes, or if there
is no good reason for it, or if it is accompanied by headaches, dizziness,
ringing in the ears or visual impairments.
Sprain
Sprains may occur when the ligaments
around the joints are overstretched. Bruising and swelling often accompany
sprains.
What to IMMEDIATELY do: On the first day, put
ice on the injured area and change it every 20 minutes. Bandage the injured
area with an elastocrape bandage to keep the area from moving, elevate the limb
and don't move it for 24 hours. Afterwards apply heat to the area to get the
blood flowing again. Take a muscle relaxant and an analgesic orally after
meals.
What NOT to do: Do not try to 'work
through the pain', it will only get worse and you may end up doing further
damage. Ligaments thet were partially torn can get further damaged.
When to seek medical aid: If the
problem doesn't get better within a few days, go to a doctor.
First aid is a combination of simple
procedures and common sense. It is an emergency measure, generally consisting of
simple, often life-saving techniques that most people can train to perform with
minimal equipment and no previous medical experience. The term usually refers
to administering care to a human, although it can also be performed on animals.
It is not classed as medical treatment and does not replace interventions from
a trained medical professional. The aims of first aid are to preserve life,
prevent harm, and promote recovery.
I leave you today with a video of St.
John’s Ambulance on First Aid: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BQNNOh8c8ks







No comments:
Post a Comment